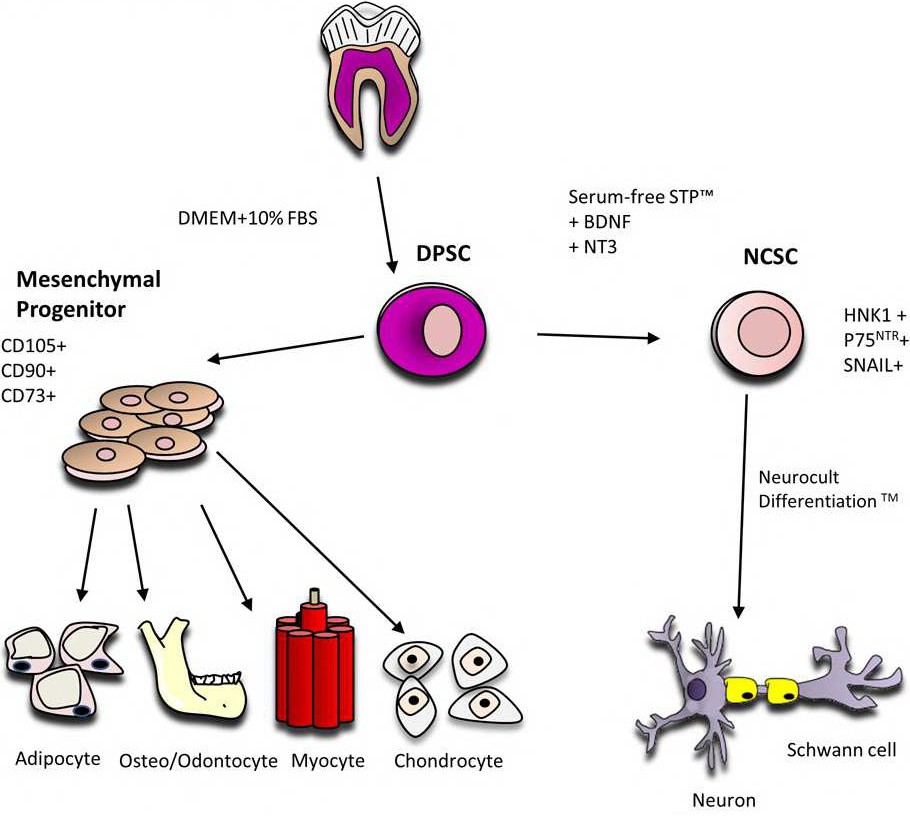
Fig. 7. Summary of research findings: Stem Cells within dental pulp tissue, collectively termed Dental Pulp Stem Cells or DPSCs, comprise actually a mixture of early HNK1+ and p75NTR+ NC progenitors, which are able to give rise to neuronal and glial cells, together with further committed ectomesenchymal stem cells, which are specialized to differentiate to connective tissue cell lineages. Under standard in vitro culture media containing FBS, hDPSCs tend to differentiate to ectomesenchymal phenotypes, characterized by the expression of CD90, CD73, CD105 and Collagen I markers. This differentiation process may be reverted by culturing hDPSCs with a serum free (STP(tm)) medium, supplemented with BDNF and NT-3 neurotrophins. Under these conditions, hDPSCs highly upregulate NC progenitor markers HNK1 and p75NTR and acquire an enhanced capacity to give rise to neuronal and glial lineage cells.